Nurkse introduces the concept of the vicious circle of poverty to elucidate the origins of poverty. This phenomenon is characterized by self-perpetuating factors that create a circular interplay, leading to the persistent cycle of poverty and underdevelopment. In Nurkse’s words, the vicious circle of poverty involves a continuous interaction of forces that contribute to maintaining a state of poverty in a given country.
Various types of these detrimental ‘vicious circles’ exist, each representing a complex network of interconnected factors that mutually reinforce and sustain the conditions of poverty.
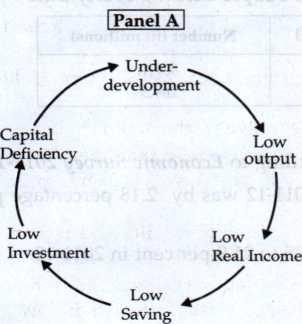
In Panel A, it is demonstrated that in an underdeveloped country, the overall output is limited, leading to a state of low real income. This, in turn, hampers the ability of individuals to save, resulting in diminished investment and a scarcity of capital formation. A country characterized by low levels of capital investment remains underdeveloped, perpetuating a recurring cycle.
In Panel B, the illustration depicts that in an underdeveloped nation, low productivity contributes to a reduced real income. This decline in income leads to a contraction in demand. Consequently, investment experiences a decline due to the diminished market size. The outcome is a deficiency in capital, reinforcing the cycle of low productivity and income in the underdeveloped country.
Objective Type Questions
1. What does Nurkse’s concept of the vicious circle of poverty involve?
A. A linear progression of poverty
B. Self-perpetuating factors creating a circular interplay
C. Wealth accumulation leading to development
D. Isolation of factors contributing to poverty
Answer: B
2. According to Nurkse, what is the continuous interaction in the vicious circle of poverty aimed at maintaining?
A. Economic stability
B. High income levels
C. State of poverty
D. Technological advancements
Answer: C
3. How does limited overall output contribute to the vicious circle of poverty in Panel A?
A. It increases real income
B. It boosts investment
C. It leads to low real income
D. It has no impact on the cycle
Answer: C
4. In Panel B, what role does low productivity play in the underdeveloped nation’s cycle of poverty?
A. It accelerates economic growth
B. It increases market size
C. It leads to a reduction in real income
D. It promotes investment
Answer: C
5. What is the common characteristic of various types of ‘vicious circles’ discussed in the context of poverty?
A. Isolation of factors
B. Complex network of interconnected factors
C. Linear progression
D. Rapid development
Answer: B