Problem of unemployment creates many social and economic adverse effects on the economy.
(See flow chart in Fig 7.1).
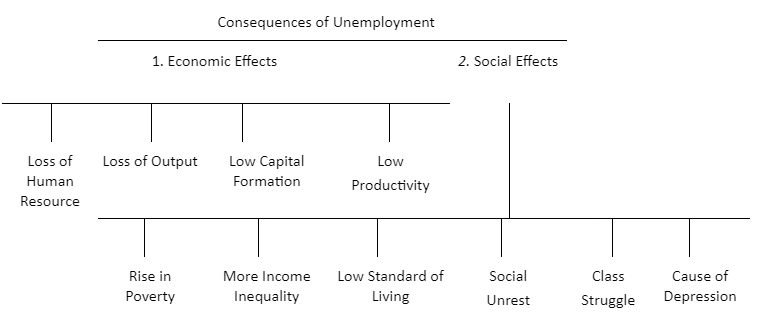
Fig. 7.1 Adverse Effects of Unemployment
Economic Effects:
(i) Loss of Human Resource:
- In a situation where people want to work but can’t find jobs, we lose valuable human resources. This means that capable and willing individuals remain unemployed, which is a waste of manpower.
(ii) Loss of Output:
- The economy suffers because it doesn’t use its human resources effectively. This leads to a drop in the level of output, national income, and the rate of growth. When people are not employed to their full potential, the economy cannot produce as much as it could.
(iii) Low Capital Formation:
- Capital formation, which is crucial for a country’s development, relies on factors like investment and saving. Saving, in turn, depends on the ability, willingness, and opportunity to save, all of which are tied to income. Unemployed people do not earn, resulting in no savings and a decline in capital formation.
(iv) Low Productivity:
- Lack of job opportunities, population growth, and the decline of small industries create pressure on resources like land. This leads to low productivity, and when productivity is low, the per capita output decreases, causing a low per capita income and a slow growth rate in the economy.
Social Effects:
(i) Rise in Poverty:
- Unemployment and poverty go hand in hand. Without a job, a person contributes nothing to production and depends on others for basic needs. This, in turn, leads to poverty.
(ii) More Income Inequality:
- Higher levels of unemployment result in greater inequality in the distribution of income and wealth in the economy. This undermines the goal of achieving ‘growth with social justice’ in economic planning.
(iii) Low Standard of Living:
- Unemployment diminishes the quality of life. Unemployed individuals struggle to meet their day-to-day needs, creating a state of ongoing hardship.
(iv) Social Unrest:
- Unemployment negatively impacts the peace of a society. It can lead to various social issues like theft, crime, deception, and a general sense of gloom.
(v) Class Struggle:
- Unemployment divides society into two groups – the rich and the poor. This division often results in class conflicts and societal tensions.
(vi) Cause of Depression:
- Unemployment is a severe problem that brings about feelings of worthlessness and frustration for those who want to work but cannot find a job. It can lead to starvation for the families of unemployed individuals.
Objective Type Questions
- What is the primary consequence of unemployment described as a “loss of human resource”?
A. Increased productivity
B. Valuable manpower going to waste
C. Rise in national income
D. Enhanced job opportunities
Answer: B - How does unemployment affect capital formation in a country?
A. Increases investment
B. Boosts savings
C. Leads to a decline in capital formation
D. Accelerates economic growth
Answer: C - What is the result of low productivity caused by unemployment?
A. High per capita income
B. Increased job opportunities
C. Low per capita output
D. Accelerated economic growth
Answer: C - According to the passage, how does unemployment contribute to more income inequality?
A. By reducing the number of jobs
B. By increasing the level of poverty
C. Through greater distribution of wealth
D. By creating class conflicts
Answer: D - What social impact does unemployment have, as mentioned in the passage?
A. Improved peace and harmony
B. Rise in social justice
C. Increased criminal activities and societal tension
D. Enhanced quality of life
Answer: C